溫故知新系列之 Propeller System
呢個禮拜就睇下Propeller System
Fixed-Pitch Propeller
Low Pitch (high rpm) for climb
High Pitch (low rpm) for cruise
The climb propeller has a lower pitch, therefore less drag. Less drag results in higher rpm and more horsepower capability, which increases performance during takeoffs and climbs but decreases performance during cruising flight.
The cruise propeller has a higher pitch, therefore more drag. More drag results in lower rpm and less horsepower capability, which decreases performance during takeoffs and climbs but increases efficiency during cruising flight.
Constant Speed Prop
How airspeed or throttle setting affect the blade angle?
Once a specific rpm is selected, a governor automatically adjusts the propeller blade angle as necessary to maintain the selected rpm.
For example, after setting the desired rpm during cruising flight, an increase in airspeed or decrease in propeller load causes the propeller blade angle to increase as necessary to maintain the selected rpm. A reduction in airspeed or increase in propeller load causes the propeller blade angle to decrease.
DA42 Propeller System
Why the blade is twisted?
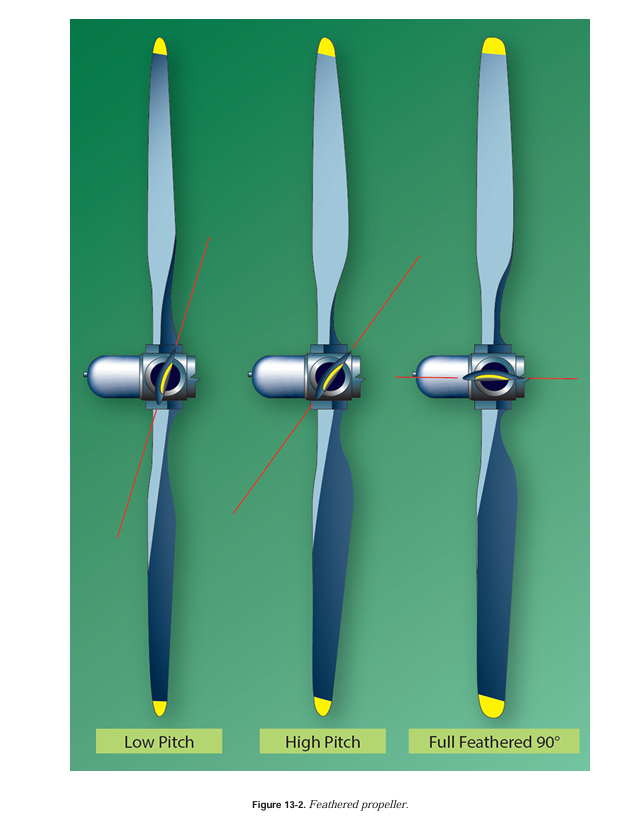
Fine, Course, Feather?
- Feathering propellers must be used on multi-engine aircraft (with constant-speed propeller) to reduce propeller drag to a minimum under one or more engine failure conditions.
- the propeller blade angle parallel to the line of flight (approximately 90°)
- With the blades feathered, the propeller stops turning and minimum windmilling
- Feathering is important because of the change in parasite drag with propeller blade angle.
Important Concept: single-engine airplanes v.s multiengine airplanes
(Ref : Airplane Flying Handbook (FAA-H-8083-3C) Chapter 13)
As a review, the constant-speed propellers on almost all single-engine airplanes (Hartzell propellers) are of the non-feathering, oil-pressure-to-increase pitch design. In this design, increased oil pressure from the propeller governor drives the blade angle towards high pitch, low rpm.
In contrast, the constant-speed propellers installed on most multiengine airplanes are full feathering, counterweighted, oil-pressure-to decrease-pitch designs. In this design, increased oil pressure from the propeller governor drives the blade angle toward low pitch, high rpm—away from the feather blade angle. In effect, the only thing that keeps these propellers from feathering is a constant supply of high-pressure engine oil. This is a necessity to enable propeller feathering in the event of a loss of oil pressure or a propeller governor failure.
當兩個引擎既飛機,失去一邊引擎時,吾feather 就姐係在windmill 情況 (low pitch, high rpm)…反而會create 好大既drag, 所以設計上要做到用engine 轉先會有油去set the blade to low pitch (high rpm) – 即無油變feather (high pitch, low rpm, reduce drag).
單引擎用constant speed propeller (e.g Hartzell propellers),佢既運作同大多數雙引擎既constant speed propeller 運作原理相反!!!
當Enginge 轉就會有oil, 反而是用oil to set the blade to high pitch angle (low rpm, reduce drag) – e.g during cruise…呢類propeller 係無油時候反而會去windmilling 狀態,即 low pitch (high rpm), 雖然好大drag, 但間接用drag (aerodynamic force) 去做類似hand prop既動作, 睇下可吾可以restart 個engine, 如果吾得某程度上就因為design 會做成好大既drag!
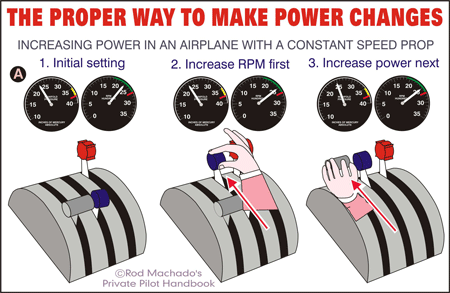
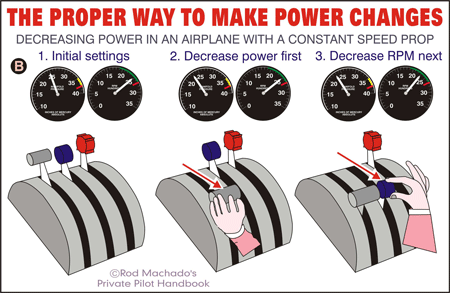
經常都講…揸constand speed prop 既機好講究rpm lever 先定 throttle lever 先…網上就教 “Keep the Prop on Top” Principle
所以Increasing power 就 右至左 ; 反之 Decreasing power 就左到右 — 咁就會做到 rpm control on top
至於點解…就係我永遠想做到係用engine 推個prop 而不是反轉黎…
https://krepelka.com/fsweb/lessons/commercial/commerciallessons01.htm
When both manifold pressure and rpm need to be changed, avoid engine overstress by making power adjustments in the proper order:
- When power settings are being increased —increase rpm first, then manifold pressure.
- When power settings are being decreased, reduce manifold pressure before reducing rpm.
(If rpm is reduced before manifold pressure, manifold pressure automatically increases, possibly exceeding the manufacturer’s tolerances.) - To prevent damage to radial engines, minimize operating time at maximum rpm and manifold pressure, and avoid operation at maximum rpm and low manifold pressure.
Archives
- February 2026
- January 2026
- December 2025
- November 2025
- October 2025
- September 2025
- August 2025
- July 2025
- June 2025
- May 2025
- April 2025
- March 2025
- January 2025
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- July 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- August 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- September 2019
- June 2019
- May 2019
- April 2019
- March 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- May 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- June 2017
- March 2017
- January 2017
- December 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- June 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- March 2014
- September 2013
- August 2013
- March 2013
- September 2012
- August 2012
Categories
- AFTC training
- AGK – Airframe, Engine, System
- AGK – Instruments
- ATPL Knowledge
- Aviation
- Aviation English
- BAK
- BC Life in CTB
- Book Sharing
- Books of OSH
- Cathay Pacific
- CNY Trip 2019
- CNY trip 2020 (Malaysia)
- Coffee
- Communication
- Corporate Governance
- English Learning
- Environmental Management
- ERM (enterprise risk management)
- Excel
- First Step Summit
- Flight International (Magazine)
- Flight planning and Monitoring
- HKMA ADMS
- Human Performance and Limitations
- Introduction to OHS
- IT
- Korea Trip 2019
- Learn from aviation accident
- Legislative Context in OHS
- London + Paris 2013
- Macau @ Trip 2017
- Meteorology
- Microsoft Windows
- MOLDOVA CHALLENGE
- My Diaries
- My Travels
- Navigation
- Occupational Health and Safety (OSH)
- Operational Procedures
- Operations Management
- Organizational Behavior
- OSH English
- Power BI
- Preparation
- Principal of Flying
- Python
- Quality Management System (QMS)
- Radio Navigation
- Regulations, Rules and Practices
- Risk Assessment
- Road to be an airline cockpit crew
- Route Training
- Summer Trip 2018
- Taiwan trip 2016
- The life in VHHH
- The road to be a pilot
- The road to be a RSO
- Uncategorized
- Weight & Balance
- Wine
- 學車 in CTB
- 私牌系列
- 馬來西亞 (怡保+檳城) 2024